Odds ratio vs relative risk when to use Odds ratio vs relative risk reddit Statistics Quantifying the association between two events a probability report (or) is a statistism that quantifies the strength of the association between two events, A and BThe ratio of these is the risk ratio, a relative measure of association Risk Ratio = CI e /CI u = 090/058 = 155 Interpretation Smokers had 155 times the risk of respiratory disease compared toIt is defined as the ratio of the odds of an event occurring in one group to the odds of it occurring in another group, or to a samplebased estimate of that ratio – PowerPoint PPT presentation Number of Views 710 Avg rating30/50 Slides 12

When Can Odds Ratios Mislead The Bmj
Odds ratio vs relative risk ppt
Odds ratio vs relative risk ppt-10/9/21 The odds ratio tells us that the odds of passing the skills test is higher under the new program The relative risk tells us that the probability of passing the skills test is higher under the new program Using either metric, we can easily see that the new program is better than the old program Slide 1 Categorical Variables, Relative Risk, Odds Ratios STA 2 – Lecture #8 1 Slide 2 Categorical Variables The raw data from categorical variables consist of group




Ppt Odds And Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
The odds ratio will estimate the average change in odds (the average odds ratio) among exposed individuals only when all individual odds ratios are equal and all individual outcome risks without exposure are equal 1;Risk, and related measures of effect size (for categorical outcomes) such as relative risks and odds ratios, are frequently presented in research articles Not all readers know13/6/21 8/6/19 Relative risk is used in randomized controlled trials and cohort studies Relative Risk is calculated by dividing the probability of an event occurring for group1 divided by the probability of an event occurring for group2 Relative Risk is very similar to Odds Ratio, however, RR is calculated by using percentages, whereas the Odds Ratio isI don't think it > Relative measures of effect are risk ratio (ie the ratio between two incidence proportions), incidence rate ratio (the ratio between two incidence rates), and OR (the ratio between two odds) The risk difference is an absolute measure of effect (ie the risk of the outcome in exposed individuals minus the risk of the same outcome in unexposed)
2/3/ How to Calculate Odds Ratio and Relative Risk in Excel How to Interpret an Odds Ratio Less Than 1 How to Interpret Relative Risk Published by Zach View all posts by Zach Post navigation Prev How to Perform Exponential Smoothing in Excel Next How to Find Class Midpoints in a Frequency DistributionAbstract and Figures Odds ratio (OR) is a statistic commonly encountered in professional or scientific medical literature Most readers perceive it as relative risk (RR), although most of24/3/21 The odds ratio (OR) is a ratio of 2 numbers, like the relative risk we have 3 options OR = 1 The odds in the first group are the same as those in the second So no evidence that drinking wine can either OR > 1 The odds of having the disease in the exposed group are higher than the unexposedRelative measures of effect are risk ratio (ie the ratio between two incidence
25/3/21 Relative Risk Ratio and Odds Ratio September 2, , 500 pm The Relative Risk Ratio and Odds Ratio are both used to measure the medical effect of a treatment or variable to which people are exposed The effect could be beneficial (from a therapy) or harmful (from a hazard)Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the obese 3) Overall, you can see that decreasing the27/2/17 The relative risk is the ratio of the risk in the exposed group to the risk in the unexposed group, as is summarized in Box 1 Depending on the study design and statistical method applied, the relative risk can be presented using different measures of effect, such as the incidence rate ratio and hazard ratio3/2/16 Lesson #11 Relative Risk and the Odds Ratio The risk of disease, given exposure, is The risk of disease, given no exposure, is The relative risk is P(D E) P(D Eâ)




Math Matters How Misinterpretation Of Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios May Influence Conclusions Academic Pediatrics




The Incidence Risk Factors And Prognosis Of Acute Kidney Injury In Adult Patients With Coronavirus Disease 19 American Society Of Nephrology
Both the odds ratio and the relative risk compare the relative likelihood of an event occurring between two groups The relative risk is easier to interpret and is consistent with general intuition Some designs, however, allow only for the calculation of the oddsIn many clinical papers, probabilities are reported both as 'risk ratios' and 'odds ratios' to indicate similar things However, they are not calculated similarly In this blog, I'll review the basic concepts behind these and examine how they differ with an exampleOdds Ratio, Relative Risk, Risk Difference Statistics Tutorial #30 MarinStatsLectures How Compelling Is Your Writing?Many healthrelated studies express results in terms of the Odds Ratio (OR), a frequentlymisunderstood statistic that resembles but differs from the Relativ




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean
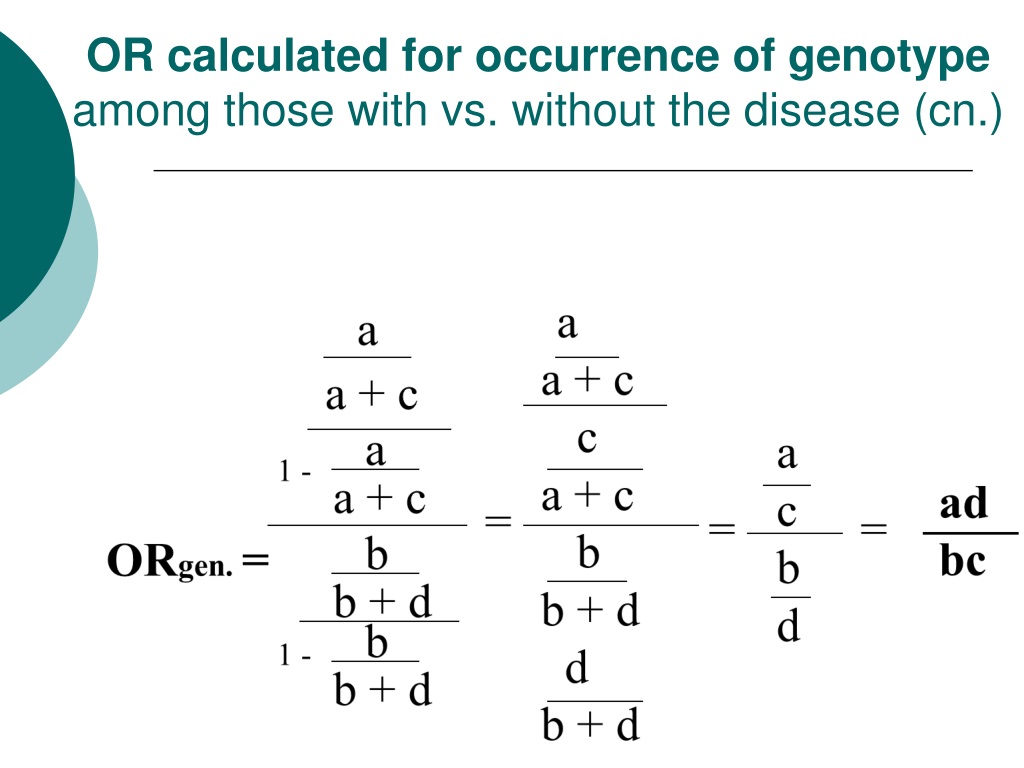



Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
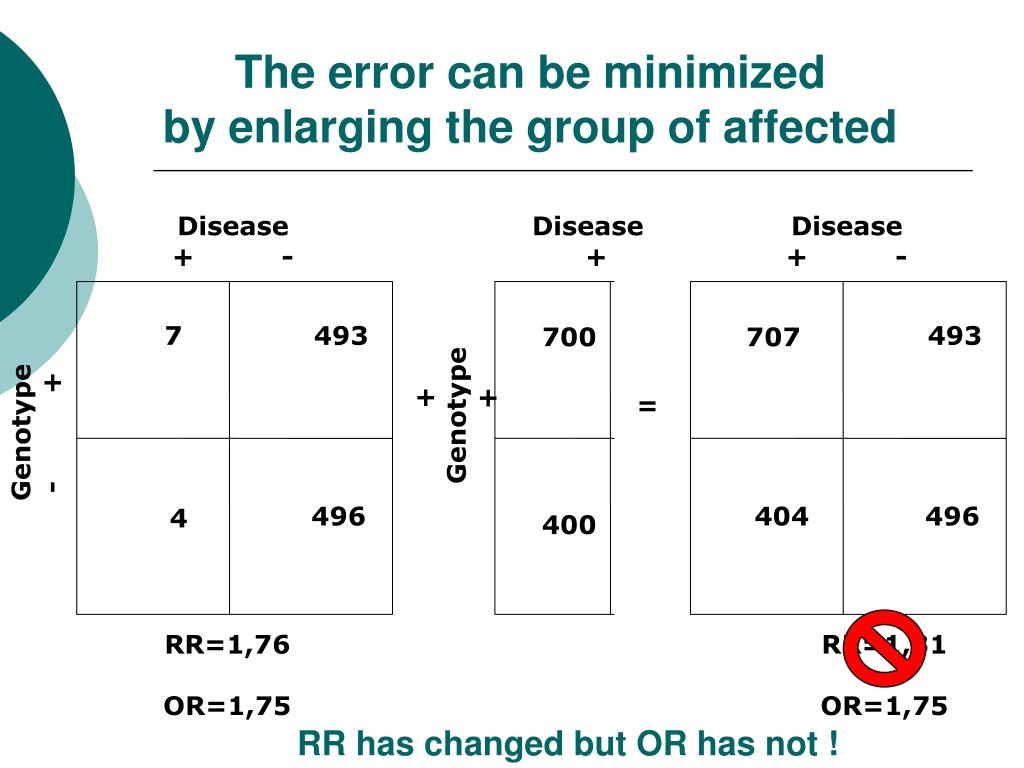
Keneeepid12 Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (ppt), PDF File (pdf), Text File (txt) or view presentation slides online fdsgWhen the disease is rare, the odds ratio will be a very good approximation of the relative risk The more common the disease, the larger is the gap between odds ratio and relative risk In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative risk OR = 0752 and RR25/7/21 2) Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the nonobese Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the obese 3) Overall, you can see that decreasing the baseline incidence will decrease the odds ratio (300 in those who are nonobese versus 129 in those who are obese) Obviously, these results run counterIn a control group The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative




Relative Measures Of Association For Binary Outcomes Challenges And Recommendations For The Global Health Researcher



Relative Risk Ratio Vs Odd Ratio Ppt Authorstream
10/6/21 The simple relative risk is 055 and the simple odds ratio is 025Clearly the probability of fathering a child is strongly dependent on a variety of demographic variables, especially age (the issue of marital status was dealt with by a separate analysis) The control group was 84 years older on average (435 years versus 351), showing the need to adjust for this variable Odds ratioThat odds ratios will closely approximate risk ratios But if risk ratios are desired when outcomes are common, odds ratio estimates will not suffice In this article, I describe methods for estimating adjusted risk ratios with confidence intervals (CIs) in Stata P Cummings 177Ppt Categorical Variables Relative Risk Odds Ratios Ppt Categorical Variables Relative Risk Odds Ratios Ppt Week 7 Usmle Step 1 Review Biostatistics Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Ppt Biostatistics Breakdown Common Statistical Tests



Odds Ratio




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Kidney International
Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the obese 3) Overall, you can see that decreasing the baseline incidence will decrease the odds ratio (300 in those who are nonobese versus 129 in those who are obese) Obviously, these results run counter to expected results, putting the onus on the researcher to justify them Similarly, you should find that increasing the incidence will increase the odds ratioThe Relative Risk Ratio and Odds Ratio are both used to measure the medical effect of a treatment or variable to which people are exposed The effect could be beneficial (from a therapy) or harmful (from a hazard) Risk is the number of those having the outcome of interest (death, infection, illness, etc) divided by the total number exposed to Hazard Ratios vs Risk Ratios (or Relative Risk24/2/13 ODDS RATIO An odds ratio is the odds of the event in one group , for example, those exposed to a drug, divided by the odds of the event in another group not exposed Odd ratio in epidemiology In case control study since the incidence is not available so relative risk can not be calculated directly Therefore Odd ratio is obtained which is a measure of strength of association between
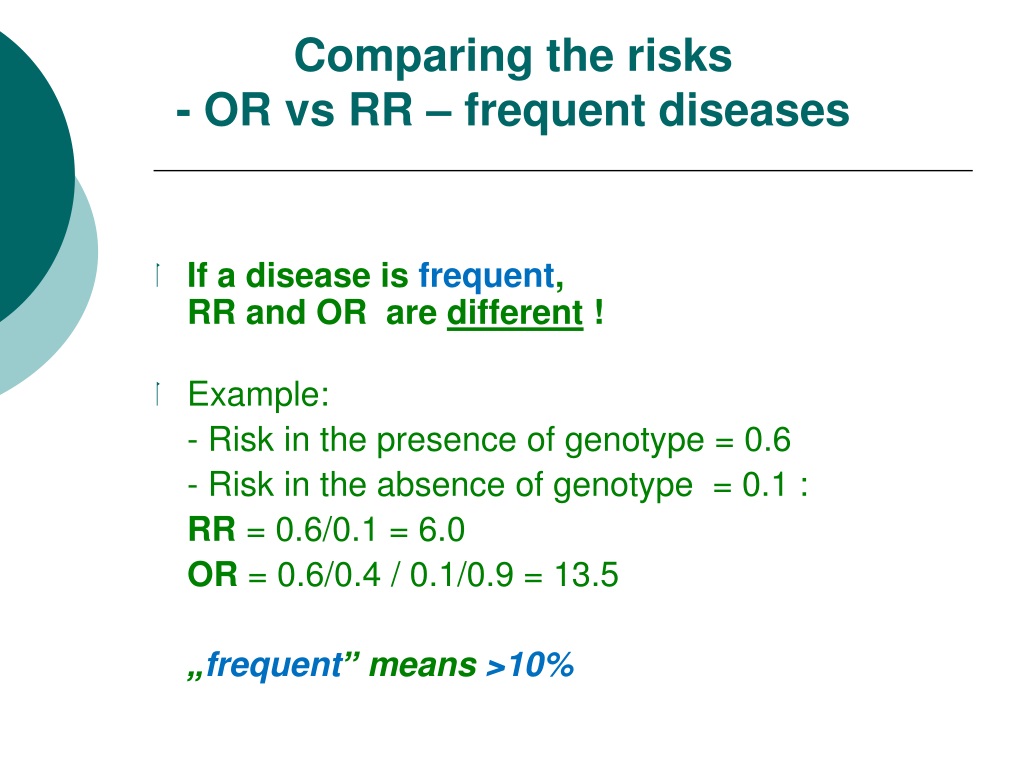



Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Dementia Prevention Intervention And Care Report Of The Lancet Commission The Lancet
15/6/21 RealRisk works with any study which investigates the link between a risk factor or intervention and an outcome of interest, which also reports one of the following a relative risk (RR), hazard ratio (HR), odds ratio (OR) or a percentage change The study can be observational or experimental in design The terminology used can vary – so don't be put off if the terms 'riskThe risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a) For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effects are the same for both interventionsThe odds ratio in this study, is simply the odds of smoking among those with lung cancer, divided by the odds of smokingOdds ratio and risk ratio are related concepts that can be interchanged when the prevalence of the effect is low, but not in other situations The realm of science is full of trapsA prevalence ratio, or ;




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Kidney International




Relative And Attributable Risks Ppt Download
23/5/21 For estimates of relative risk ratios, this becomes logarithm We can specify this manually, or just use a builtin family for our generalized linear model for which the logarithm is the canonical link fucntion, and hence the defaultTable 1 Relative risk (RR) vs Odds Ratio (OR) vs Hazard Ratio (HR) HRs are in tandem with survivorship curves, which show the temporalERRATA At about the 300 mark the slide says "10,00" when it is really supposed to say "10,000" I added a pop up box to fix it Thanks to Mehdi Hedjazi forIn a control group The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group An RR or OR of 100 indicates that the risk is comparable in the two groups A value greater than 100 indicates increased risk;
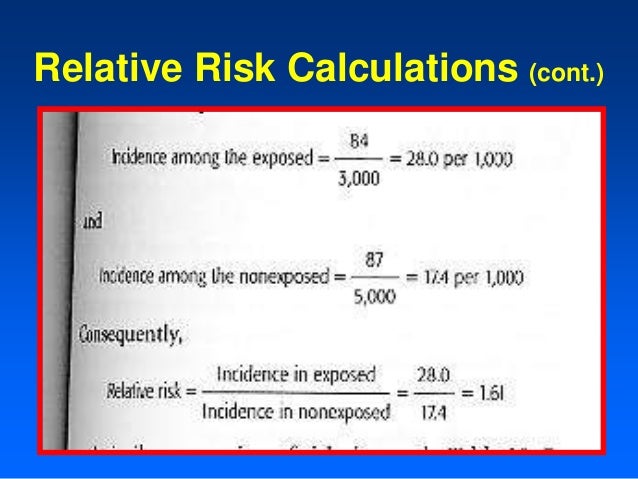



Relative And Atribute Risk




Relative And Atribute Risk
27/4/21 Odds ratio vs relative risk formulaOdds ratios work the same An odds ratio of 108 will give you an 8% increase in the odds at any value of X Likewise, the difference in the probability (or the odds) depends on the value of X So if you do decide to report the increase in probability at different values of X, you'll have to do it at low, medium, and high values of XUnless I'm15/9/21 RELATIVE RISK AND ODDS RATIO The relative risk (also known as risk ratio RR) is the ratio of risk of an event in one group (eg, exposed group) versus the risk of the event in the other group (eg, nonexposed group) The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of odds of an event in one group versus the odds of the event in the other groupHow To Calculate Relative Risk 3 Steps With Pictures Wikihow Odds ratio vs relative risk usmle



Relative Risk Ratio Vs Odd Ratio Ppt Authorstream




Figure1 The Bmj
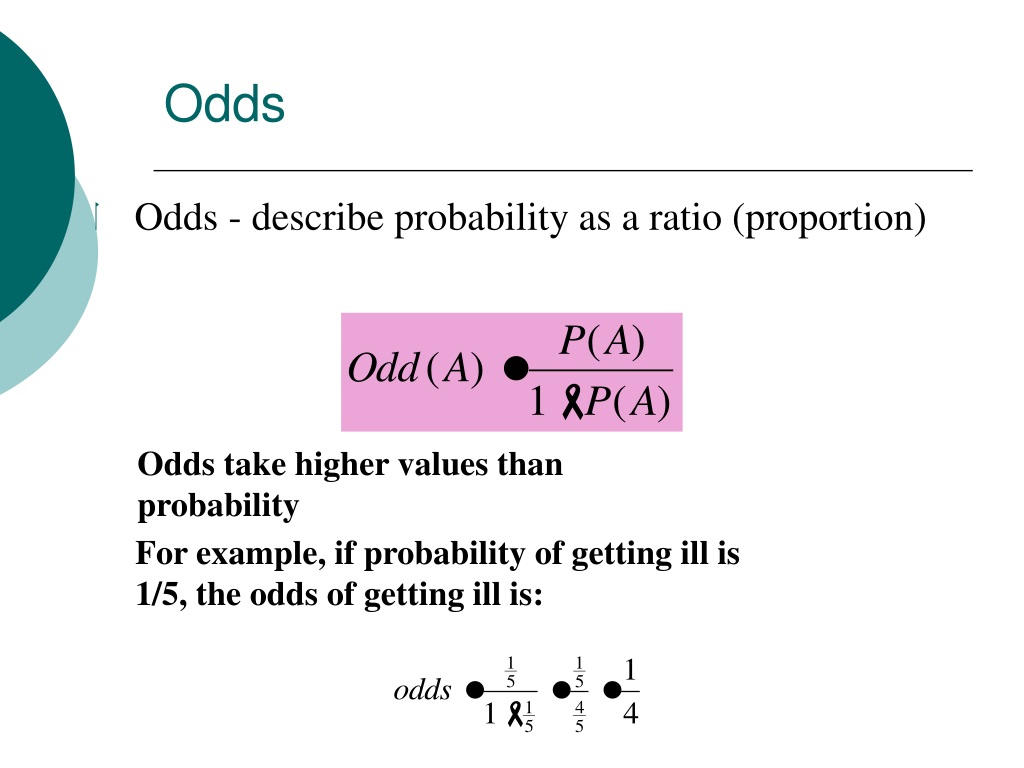
Odds and Odds Ratios Odds = p/(1p) The odds of a man receiving SAT is 053/(1 053) = 113 The odds of a woman receiving SAT is 062/(1 062) = 163 Odds Ratio = 163/113 = 144 Interpretation "A woman is 144 times more likely to receive SAT than a man"Odds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a rWe see that the 'relative risk' is now different, but the odds ratio does not change if we change the ratio of cases versus controls Until now we have learned the following 1 we can calculate relative risk IF we can estimate probabilities of an outcome in EACH group 2 we can't do that in case control studies



Hazard




Dynamic Lines Measures Of Association N Absolute Risk The Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Provide A Measure Of Risk Compared With A Standard N Attributable Ppt Download
11/7/16 The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example Relative Risk/Risk Ratio Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring programPalabras clave Odds ratio, Riesgo relativo SUMMARY The odds ratio (OR) and relative risk (RR) are measures of association for dichotomous nominal variables The OR has been widely used for biomedical research, the reasons for this are 1) The OR determines an estimate (with confidence interval) for relations between binary dummy15/3/21 It is assumed that, if the prevalence of the disease is low, then the odds ratio approaches the relative risk Case control studies are relatively inexpensive and less timeconsuming than cohort studies In this case the odds ratio (OR) is equal to 16 and the relative risk (RR) is equal to 865




Odds Ratio




Ppt Case Study Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Powerpoint Presentation Id
An odds ratio is a useful measure of association In a cohort study, the relative risk can be calculated directly In a casecontrol study the relative risk cannot be calculated directly, so an odds ratio is used instead Attributable Risk Concept of Attributable Risk Attributable Risk for an Exposed Group Attributable Risk for an Exposed Group (cont) Calculation for Proportional Incidence in Total Population Calculations for Attributable Risks (cont) Summary Relative risk and odds ratioA value lower than 100 indicates decreased risk The 95% confidence intervals and statisticalThe odds ratio here Interpretation of the odds ratio The odds ratio will always be bigger than the corresponding risk ratio if RR >1 and smaller if RR




Relative And Atribute Risk




Ppt Point Estimation Odds Ratios Hazard Ratios Risk Differences Precision Powerpoint Presentation Id
26/8/ Odds ratios While risk reports the number of events of interest in relation to the total number of trials, odds report the number of events of interest in relation to the number of events not of interest Stated differently, it reports the number of events to nonevents
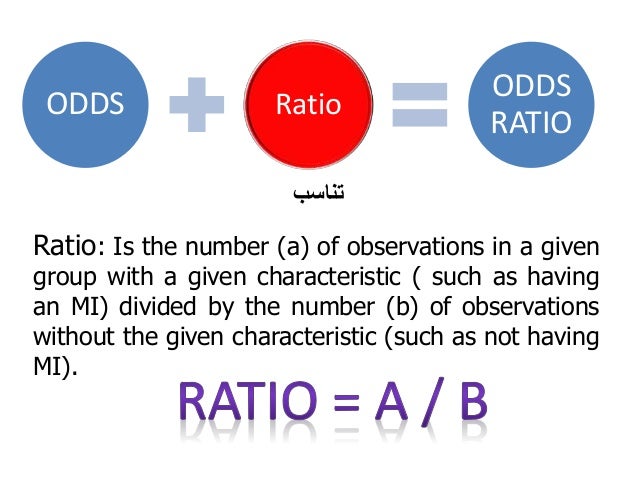



Odds Ratios Basic Concepts




Relative And Atribute Risk




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Model Example Cpb Presentation Graphics Presentation Powerpoint Example Slide Templates




Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
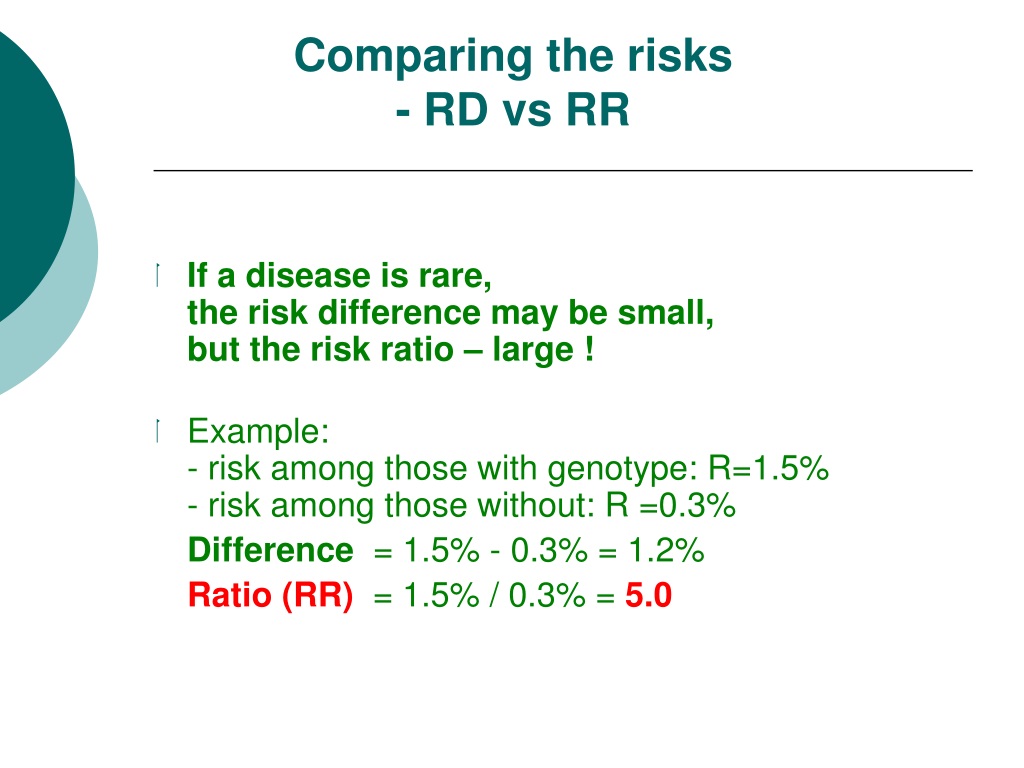



Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Against All Odds Improving The Understanding Of Risk Reporting British Journal Of General Practice
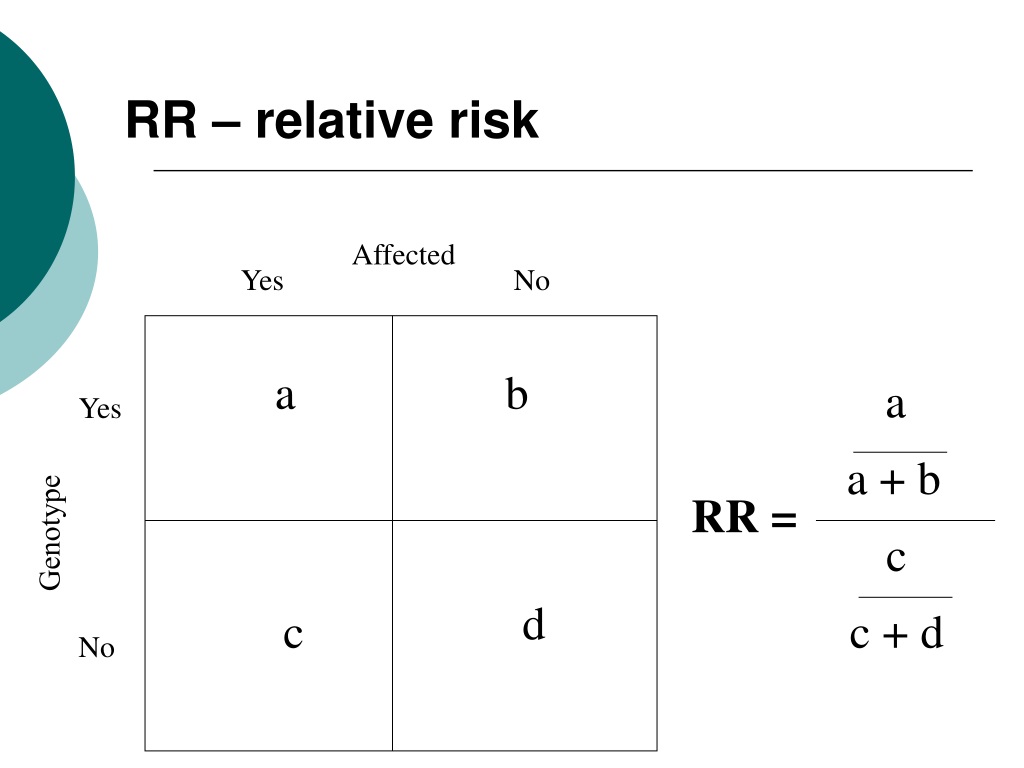



Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Ppt Odds And Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




Critical Numbers Living With Risk Ppt Download
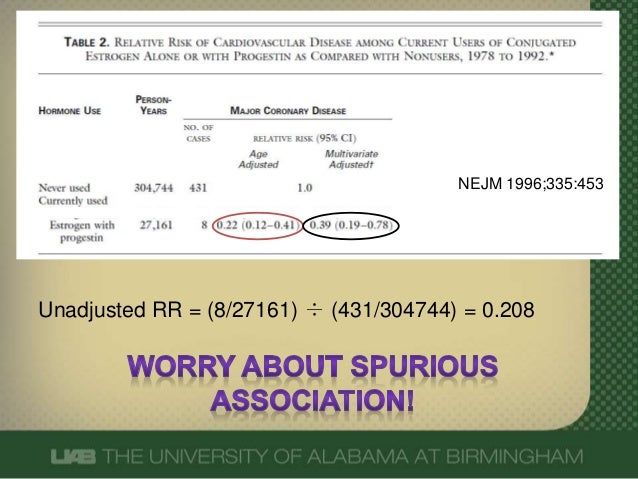



What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean



Risk Of Cardiovascular Disease From Antiretroviral Therapy For Hiv A Systematic Review




Dementia Prevention Intervention And Care Report Of The Lancet Commission The Lancet




Odds Ratio
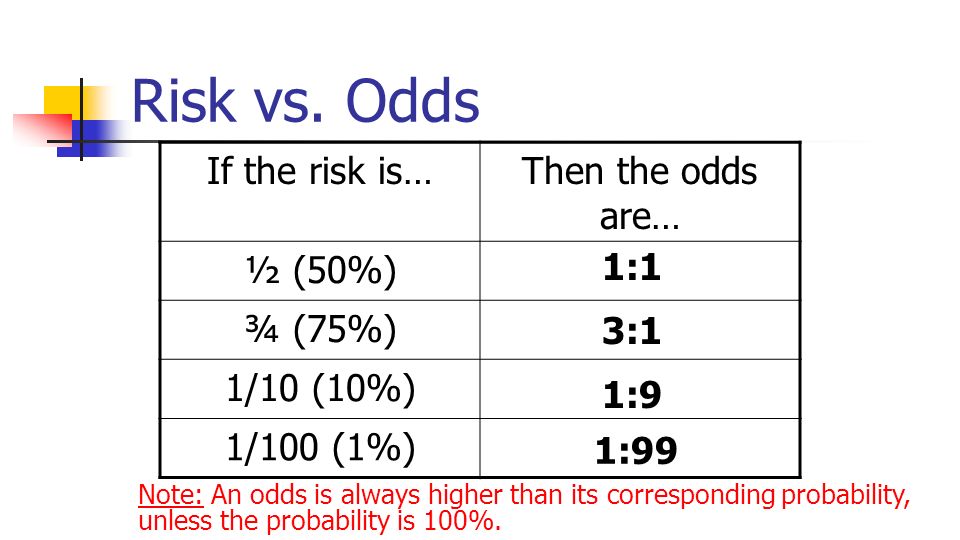



印刷可能 Odds Vs Risk ただの悪魔の画像



Relative Risk Ratio Vs Odd Ratio Ppt Authorstream




Relative And Attributable Risks Ppt Download
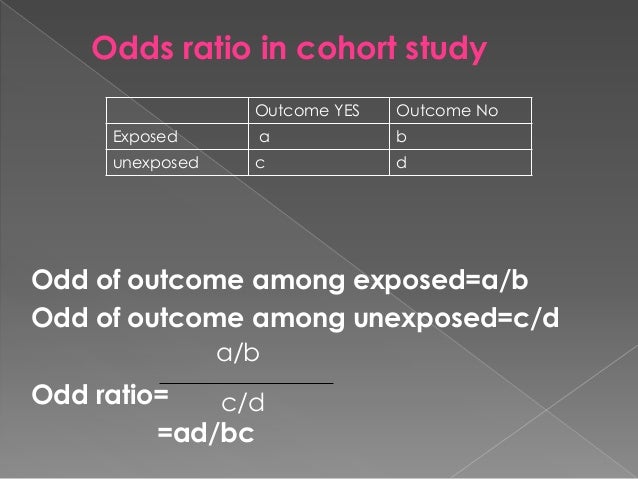



Odds Ratio




Risk Ratio A Risk Ratio Or Relative Risk Compares The Risk Of Some Health Related Event Such As Disease Or Death In Two Groups The Two Groups Are Typically Ppt Download




Ppt Absolute Relative And Attributable Risks Powerpoint Presentation Id
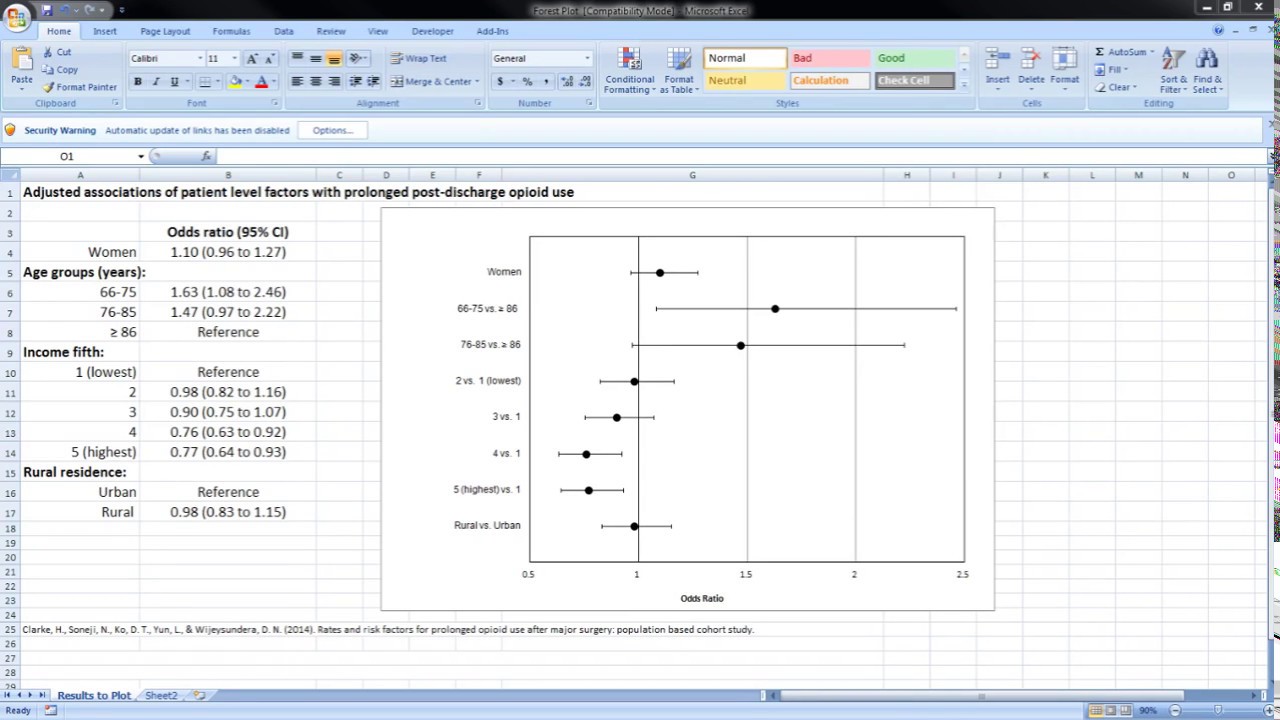



Microsoft Excel Forest Plots Odds Ratios And Confidence Intervals Youtube




What Is Odds Ratio Example




Ppt Categorical Variables Relative Risk Odds Ratios Powerpoint Presentation Id
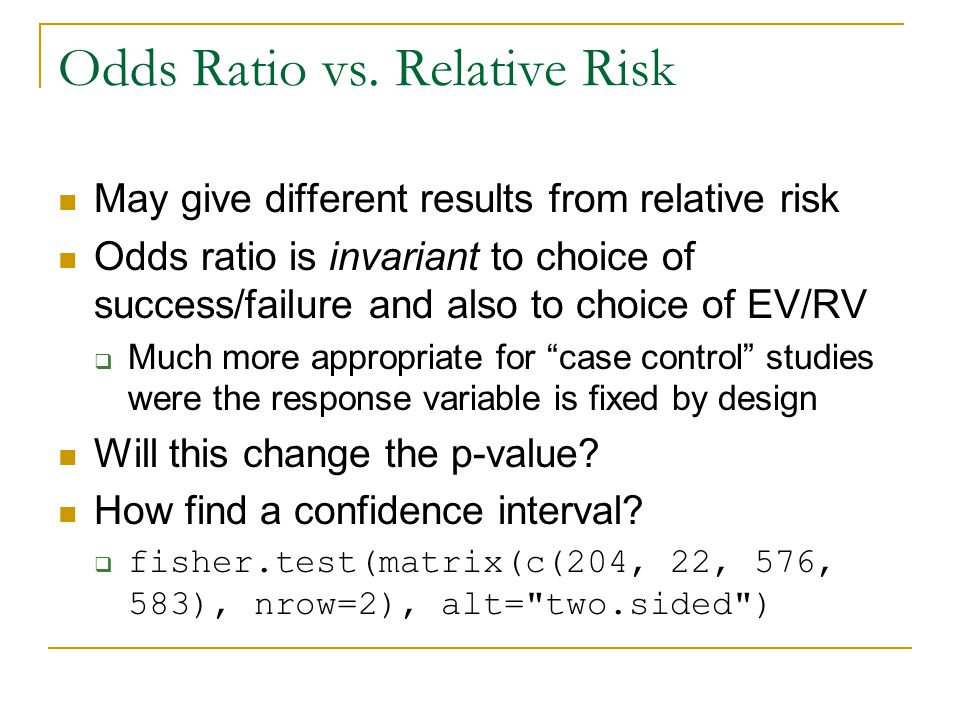



Confidence Interval For Relative Risk Ppt Video Online Download




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




Abdullah Kharbosh What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean By Ebmteacher Casecontrol Cohort T Co Shfiaepl57 عبر Slideshare
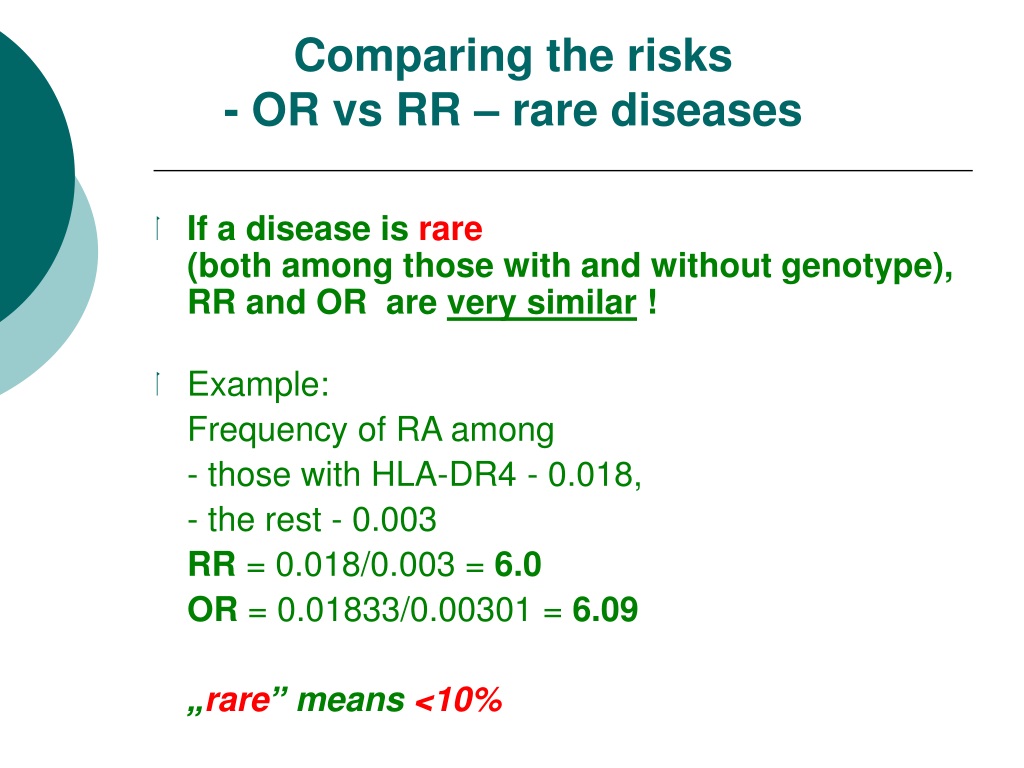



Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
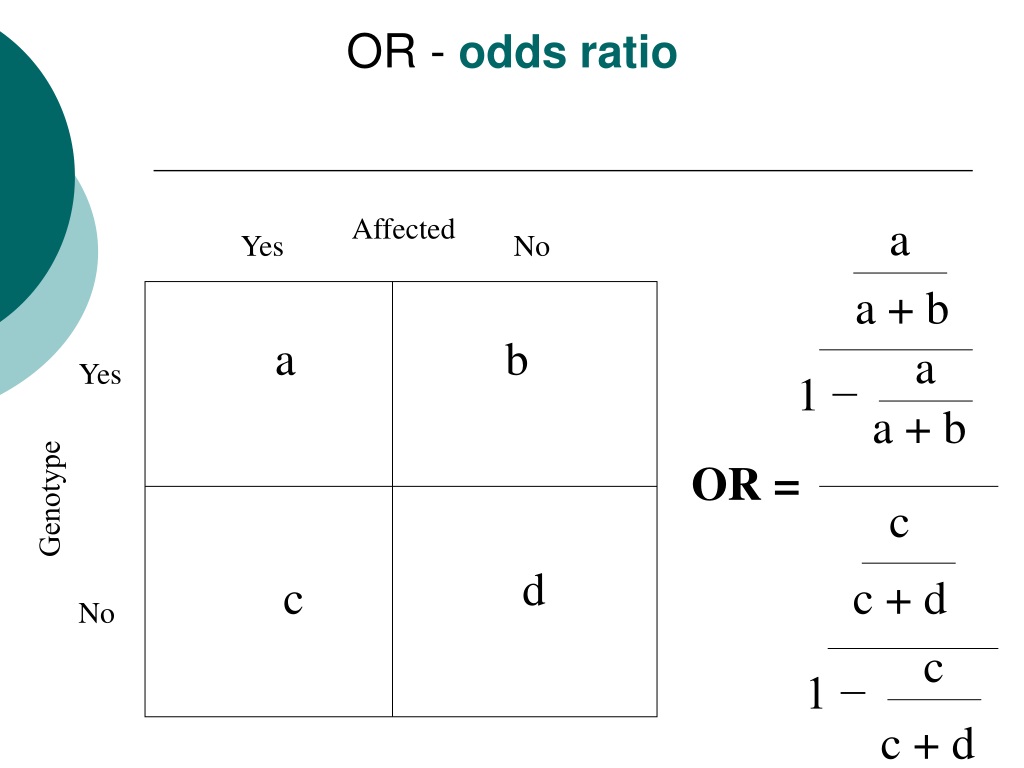



Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Three Main Types Of Nonexperimental Studies Crosssectional Compare




Ppt Odds And Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube




Measures Of Association Ppt Download




Cph Exam Review Epidemiology Ppt Download




Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Relative Risk Ratio Vs Odd Ratio Ppt Authorstream




Cph Exam Review Epidemiology Ppt Download
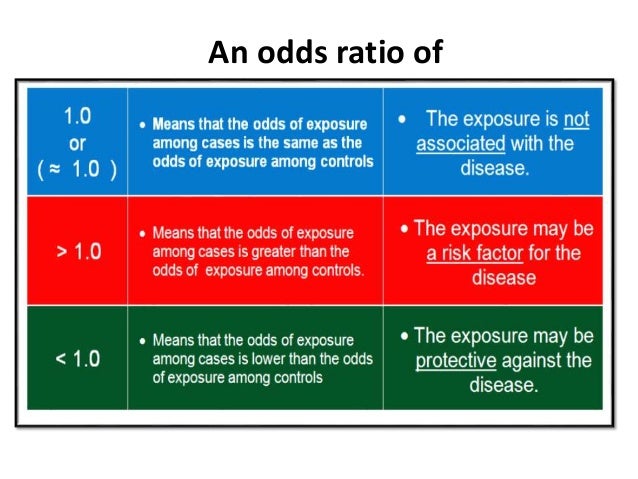



Odds Ratios Basic Concepts




Absolute Relative And Attributable Risks Outcomes Or Differences That We Are Interested In Differences In Means Or Proportions Odds Ratio Or Ppt Download




Ppt Lesson 11 Relative Risk And The Odds Ratio Powerpoint Presentation Id




Ppt Relative Risk Increased Risk And Odds Ratios Powerpoint Presentation Id
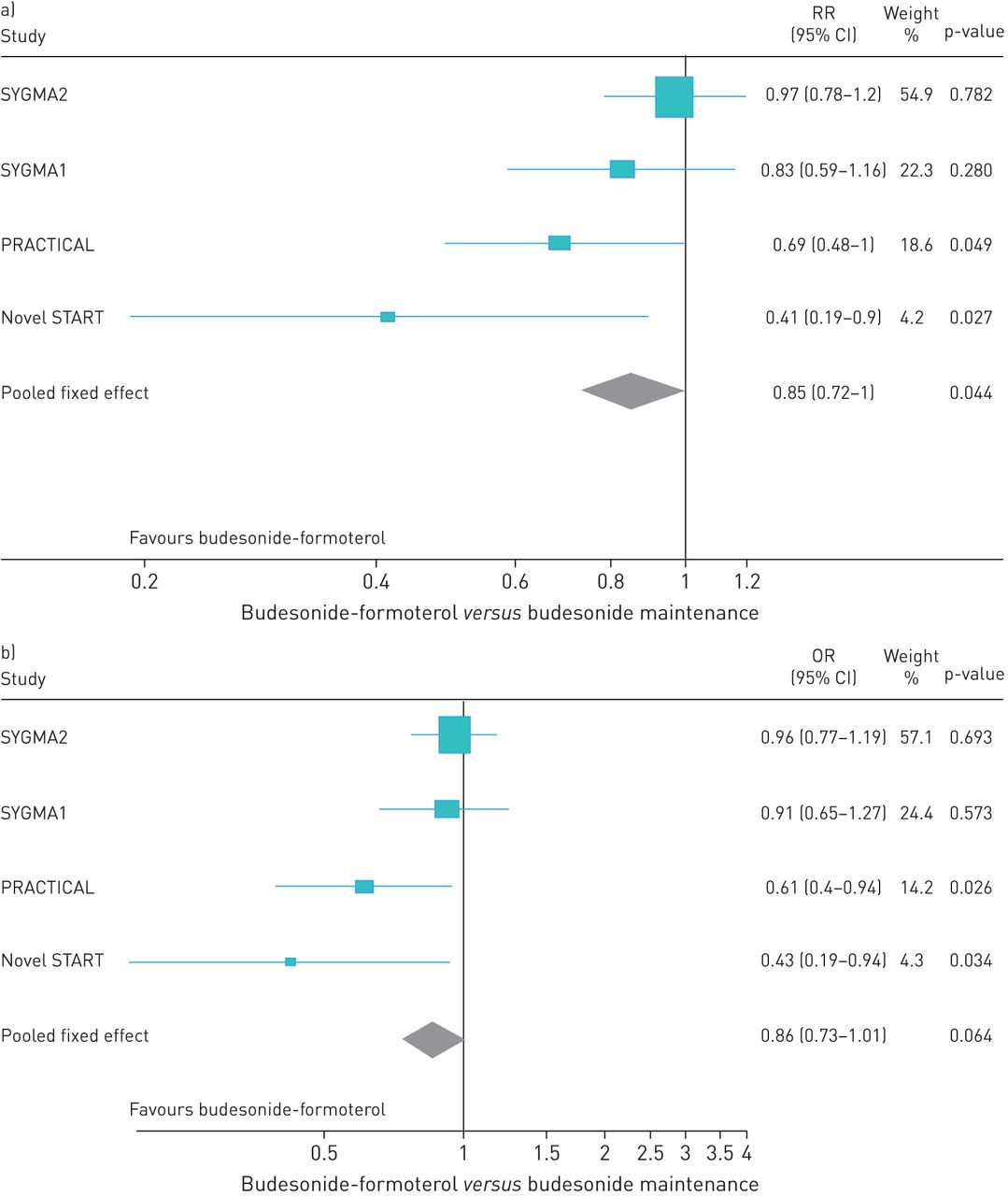



Ics Formoterol Reliever Versus Ics And Short Acting B2 Agonist Reliever In Asthma A Systematic Review And Meta Analysis European Respiratory Society



1




Map To Illustrate The Odds Ratio For 5 Year Risk Adjusted Survival Download Scientific Diagram




Odds Ratio




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Model Example Cpb Presentation Graphics Presentation Powerpoint Example Slide Templates




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




When Can Odds Ratios Mislead The Bmj
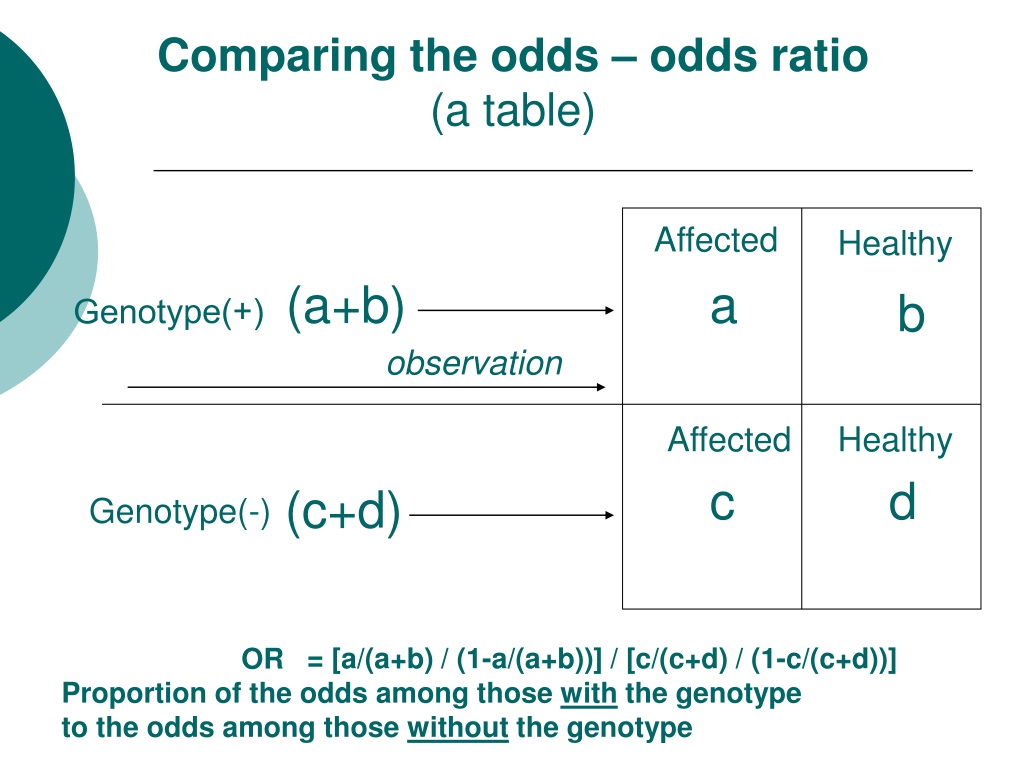



Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Racial And Ethnic Differences In Treatment And Outcomes Of Severe Aortic Stenosis A Review Jacc Cardiovascular Interventions




Relative And Atribute Risk




最新 Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Usmle ただの悪魔の画像




Questionable Utility Of The Relative Risk In Clinical Research A Call For Change To Practice Journal Of Clinical Epidemiology



Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Estimating Risk



1



Relative Risk Ratio Vs Odd Ratio Ppt Authorstream



Relative Risk Ratio Vs Odd Ratio Ppt Authorstream




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean



Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence




Abdullah Kharbosh What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean By Ebmteacher Casecontrol Cohort T Co Shfiaepl57 عبر Slideshare




Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 Ppt Video Online Download




Relative And Atribute Risk




Risk Factors For Early Onset Ischemic Stroke A Case Control Study Journal Of The American Heart Association




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio




Circulating Mirnas And Risk Of Sudden Death In Patients With Coronary Heart Disease Jacc Clinical Electrophysiology




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Model Example Cpb Presentation Graphics Presentation Powerpoint Example Slide Templates




Questionable Utility Of The Relative Risk In Clinical Research A Call For Change To Practice Journal Of Clinical Epidemiology




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean




Statistics In Medicine Ppt Download




Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 Ppt Video Online Download




Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056




Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Odds Ratio



Effect Sizes For 2 2 Contingency Tables



Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿